The Rise of Autonomous Healthcare: When AI Agents Create Real-Time Learning Systems
Bart de Witte 27 Feb 2025 • 8 min read
Today has been difficult. I just learned that one of my earliest colleagues and mentors from my time at SAP passed away from cancer at only 52. His guidance shaped my early career and understanding of healthcare technology. His untimely death reminds me why the work we do in healthcare innovation isn't just about technology – it's about saving lives and giving people more time with their loved ones. It also reinforces my conviction that we must accelerate the pace of innovation in healthcare.
For over two decades, I've been known for thinking years ahead of the curve in healthcare technology. Back in 2016, during the Data Natives conference, I predicted the disappearance of traditional EMR interfaces and the rise of conversational AI in healthcare. In 2019, I warned investors about the limitations of closed-source AI technologies and advocated for open-source approaches, predicting that development velocity would become more valuable than intellectual property, a vision that proved prescient with the DeepSeek moment that transformed the AI landscape. Many thought these predictions were overly ambitious, romanticism or even science fiction. Yet here we are, watching them materialize into reality.
Today, as we stand at another inflection point, I want to share an even bolder vision of the future, one where autonomous healthcare systems powered by interconnected AI agents create real-time learning networks that fundamentally transform care delivery. Just as the shift toward open source has accelerated AI innovation beyond what closed systems could achieve, the move to autonomous, agent-based healthcare will catalyze improvements in care delivery at a pace we've never seen before.
Understanding Where We Are:
eHealth vs. Agentic Systems
Before we dive into the future, let's understand where we stand. Healthcare IT has evolved through two distinct paradigms that fundamentally differ in how they approach patient care:
Current eHealth systems represent our first digital transformation wave, the digitization of health information through EMRs, telemedicine platforms, and patient portals. These systems form the backbone of modern healthcare IT, providing digital interfaces for healthcare professionals and patients to manage care. While revolutionary for their time, they remain fundamentally reactive, requiring human intervention for most decisions and actions.
Agentic healthcare systems, which we're just beginning to implement, represent a fundamental shift. These systems utilize AI agents as autonomous entities that can monitor health, adjust treatments, and coordinate services with minimal human intervention. The contrast between these approaches is striking across multiple dimensions:
In terms of primary focus, while eHealth systems are application and interface-based, requiring users to drive actions, agentic systems are AI-driven and proactively initiate care processes. Consider scheduling: eHealth systems wait for someone to book an appointment, while agentic systems can identify care needs and initiate scheduling automatically.
Agentic healthcare systems, which we're just beginning to implement, represent a fundamental shift. These systems utilize AI agents as autonomous entities that can monitor health, adjust treatments, and coordinate services with minimal human intervention. Crucially, these systems communicate with clinicians through personalized AI assistants that act as intelligent intermediaries – translating complex data streams into actionable insights and keeping healthcare providers informed for critical clinical decisions. Instead of drowning in data, clinicians receive curated, contextualized information that supports their decision-making process.
To illustrate the differences, consider the following table:
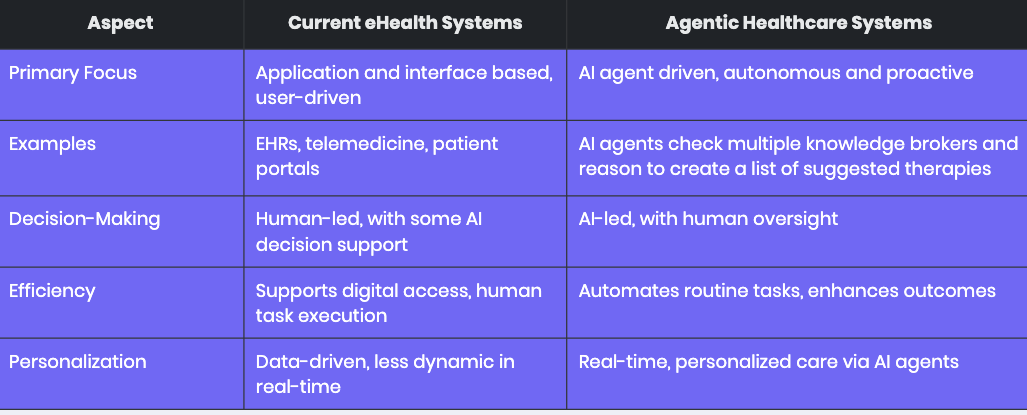
The contrast between these approaches is striking across multiple dimensions:
- Autonomy and Proactivity: The decision-making process differs dramatically. Traditional EMRs require manual data entry and review, with humans leading decisions supported by some AI tools. In contrast, agentic systems can autonomously adjust treatments within safe parameters while maintaining human oversight.
- Efficiency and Outcomes: Efficiency gains also separate these approaches. While eHealth systems enhance efficiency through digital access and streamlined workflows, they're still limited by human interaction speed and decision-making capacity. Agentic systems can reduce healthcare provider workload by automating tasks, potentially improving patient outcomes through early interventions.
- Personalization: personalization takes on new meaning in agentic systems. Current eHealth systems offer personalized data access but remain relatively static, often requiring manual updates or reviews. Agentic systems leverage real-time data for truly personalized care, such as using wearable data to detect early signs of disease or adjusting treatment plans based on immediate patient response.
The Dawn of Real-Time Medical Knowledge Creation
Let me paint a picture of what's coming, a future that's closer than many might think. Imagine an oncology consultation where the physician sits with their patient, but they're not alone. Working alongside them will be, an AI assistant that's part of a sophisticated network of AI agents. As they discuss the patient's tumor sequencing results, something remarkable will happen, instead of spending hours manually analyzing molecular profiles and searching through databases, the physician will receive real-time insights synthesized from biobanks, health information systems, and global clinical trial databases.
This isn't just wishful thinking. The technology components are already emerging. In this future scenario, AI agents will work in concert, analyzing complex molecular data, cross-referencing findings with research databases, identifying potential clinical trials, and generating personalized patient education materials. All orchestrated through a secure platform that maintains strict privacy standards and data governance.
What will make this system truly revolutionary is its ability to learn and adapt in real-time. Every patient interaction will enrich the system's knowledge base. When an oncologist makes a treatment decision based on molecular profiling, the outcome of that decision will feed back into the system, informing future recommendations. This will create what I call a "continuous learning loop" – where clinical practice, research, and treatment outcomes converge instantly.
The impact will extend far beyond individual care. By integrating with national health infrastructure, these systems will create a network effect where every patient interaction improves care for all patients, research insights translate immediately into clinical practice, and the boundary between research and practice becomes increasingly fluid.
But to realize this vision, we first need to address some fundamental challenges in how healthcare systems interact.
The Technical-Legal Integration Paradox 2.0
In my previous newsletter, I discussed the "technical-legal integration paradox" that plagued traditional EMR systems. Today, we face a new version of this challenge: while we have the technical capability to create autonomous healthcare systems, our legal and ethical frameworks are still catching up. But unlike the EMR era, where vendors deliberately maintained these barriers, the open nature of AI agent architectures is pushing us toward solutions. Despite these challenges, we're already seeing how autonomous systems can transform one of healthcare's most crucial areas: clinical research and knowledge creation.
From Data Silos to Knowledge Networks
Today's clinical trials are like islands of knowledge, isolated, slow to produce results, and disconnected from real-world practice. But what happens when we flip this model on its head? Here's how autonomous healthcare systems are reshaping this landscape:
- Real-Time Trial Matching Instead of researchers hunting for eligible patients, AI agents continuously scan patient populations, identifying potential trial candidates while respecting privacy through federated learning. The use of AI agents for clinical trial enrollment offers several benefits, including improved efficiency, reduced screening time, and potentially increased patient participation. For instance, ACTES at Cincinnati Children's Hospital reduced screening time by 34%, freeing up clinical research coordinators for other tasks. However, challenges include data privacy concerns, ethical considerations such as informed consent, and the need for regulatory compliance, as discussed in various articles (Artificial Intelligence Applied to clinical trials: opportunities and challenges).
- Dynamic Protocol Adaptation Traditional trials are rigid by design. But when AI agents monitor outcomes in real-time, protocols can adapt based on emerging data. Imagine a trial that automatically adjusts its parameters based on patient responses, optimizing for both safety and efficacy simultaneously.
- Bidirectional Knowledge Flow This is where it gets really interesting. Every patient interaction becomes a data point, every treatment decision a learning opportunity. AI agents don't just implement protocols – they learn from outcomes, identify patterns, and feed insights back into the system instantly.
The Autonomous Healthcare Ecosystem
The theoretical differences between eHealth and agentic systems become strikingly real when we look at emerging implementations. The recent case I witnessed at a leading research hospital in Switzerland, made me think we could build "Learning Health Networks" – a constellation of specialized AI agents working in harmony:
- Clinical Pattern Recognition Agents continuously analyze patient data, identifying subtle trends and correlations
- Trial Integration Agents match patients with appropriate studies and adapt protocols in real-time
- Knowledge Synthesis Agents combine insights from practice with existing medical literature
- Safety Monitoring Agents oversee the entire system, ensuring all actions align with medical best practices
The result? Treatment protocols that evolve in real-time, based on actual outcomes rather than historical data alone. Such systems exemplifies the shift from human-initiated actions to autonomous, proactive care management, exactly what I envisioned when I first started talking about the future of healthcare IT nearly a decade ago.
Beyond Traditional Clinical Trials
Here's a provocative thought: What if traditional clinical trials as we know them are becoming obsolete? When every patient interaction feeds into a learning health system, and AI agents can analyze outcomes across millions of cases in real-time, do we need to maintain the artificial boundary between research and practice?
Of course, we'll always need controlled studies for novel treatments. But for understanding real-world effectiveness, drug interactions, and long-term outcomes, autonomous healthcare systems offer something unprecedented: continuous, adaptive learning at scale.
Would such a system have saved my colleague's life? I don't know. His family probably doesn't know either. Cancer, like many diseases, remains a formidable opponent even with our most advanced treatments. But what I do know is that every day we wait to implement autonomous learning systems is a day we lose precious opportunities to gather insights that could save lives. Every patient interaction, every treatment outcome, every subtle pattern that might go unnoticed in our current systems, these are all pieces of a puzzle that could lead to breakthroughs in treatment.
When someone dies at 52, leaving behind a family and a legacy of mentoring others, it's natural to ask what more could have been done. While we can't change the past, we can honor those we've lost by working tirelessly to accelerate knowledge discovery and create autonomous learning systems that might help future patients. This isn't just about technology anymore, it's about giving every patient the best possible chance at more time with their loved ones.
Building the Future Today
At Isaree, we're not just theorizing about this transition, we're actively building the bridge between today's eHealth systems and tomorrow's autonomous healthcare networks. Our platform creates the infrastructure for continuous learning and adaptation, transforming static digital health tools into dynamic, intelligent systems that evolve with each patient interaction.
A Call to Action
The proliferation of AI agents in healthcare is inevitable and, in many ways, desirable. But we need to get the infrastructure right. Healthcare organizations need to start thinking about AI governance now, before the situation becomes unmanageable. We're already seeing the consequences of uncontrolled AI agent adoption in some hospitals, shadow IT practices, security vulnerabilities, and data governance nightmares. The time to act is now. We want to understand you better and have prepared a survey for you to participate in.
Bart de Witte is the founder of Isaree, a Berlin-based company building the next generation of AI-powered healthcare platforms. For over a decade, his predictions about healthcare technology have consistently preceded industry trends. For more insights into the future of healthcare IT, follow him on LinkedIn or subscribe to this newsletter.
